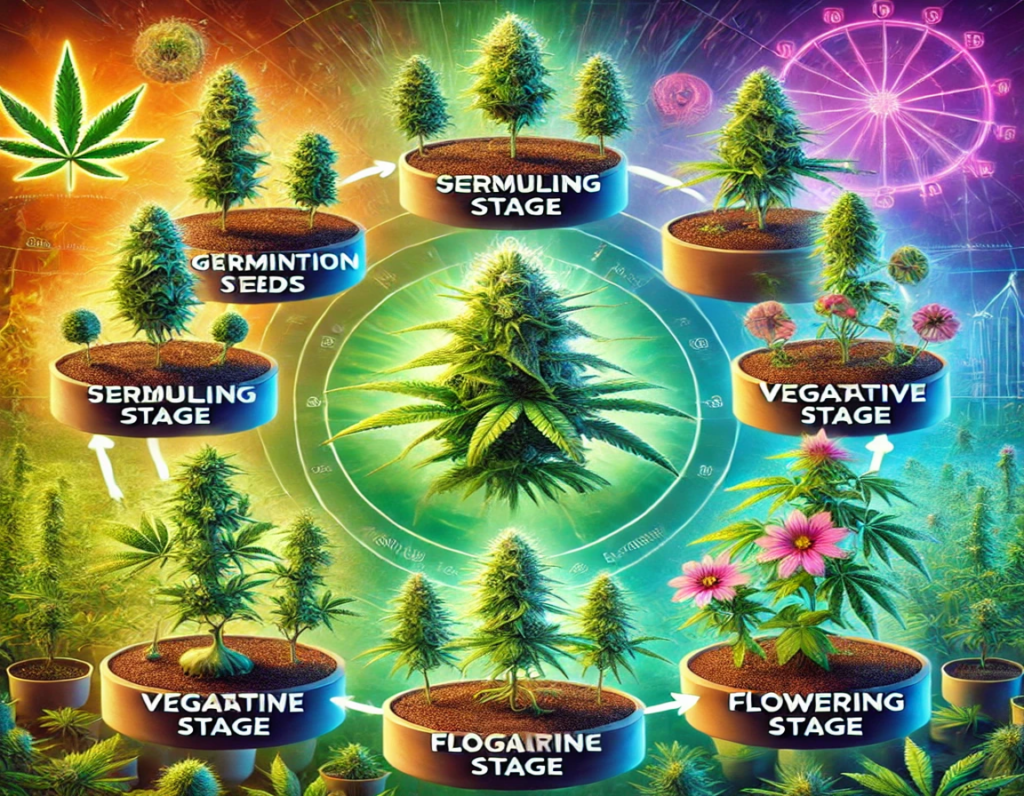
Before you can successfully harvest Green Crack seeds, it’s important to understand the entire life cycle of the plant. Green Crack is known for its rapid growth and high yield, making it a favorite among growers. The life cycle can be broken down into several key stages:
Understanding these stages will help you know when to begin monitoring your plants closely for seed development, which is crucial for maximizing your harvest.

The timing of your harvest can significantly affect the quality and quantity of the seeds you produce. In Canada, the best time to harvest Green Crack seeds generally falls in late summer to early fall, depending on your specific location and climate.
You’ll want to look for specific signs that indicate your Green Crack plants are ready for harvesting:
Keep in mind that the growing season can vary across Canada. For example, southern regions like British Columbia may see earlier harvests than northern areas. Always be mindful of your local climate conditions, as they will dictate when you should start checking your plants for maturity.

When the time comes to harvest your Green Crack seeds, employing the right techniques is essential to ensure you collect viable seeds.
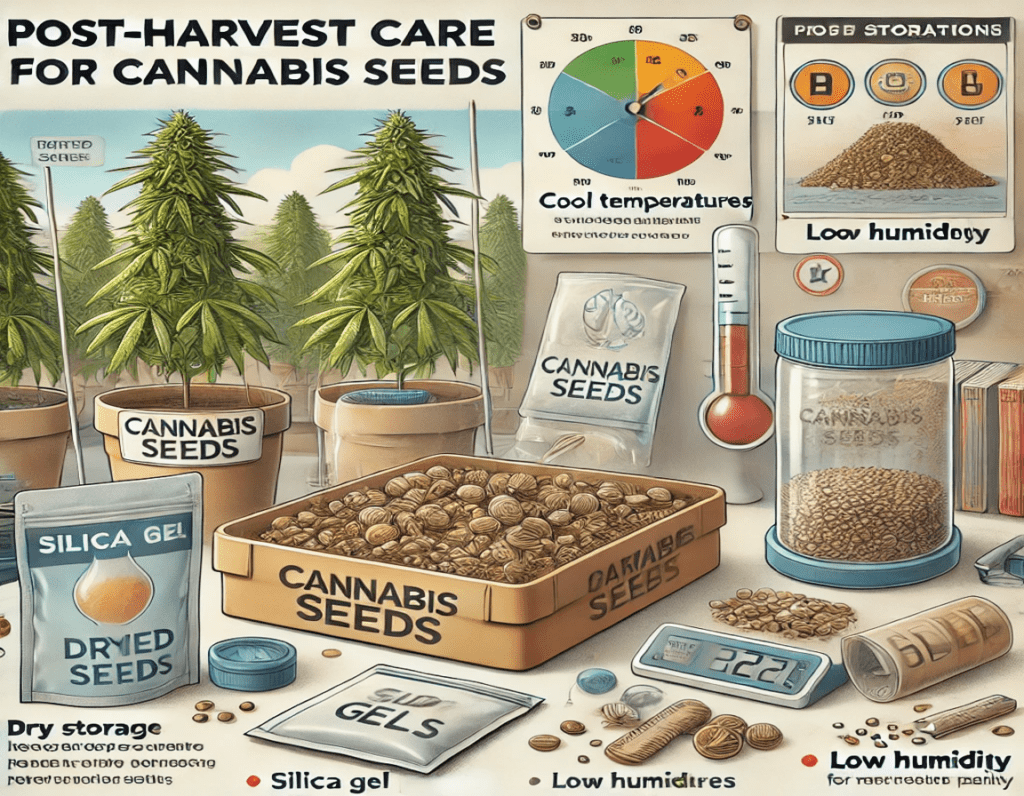
After harvesting, it’s important to care for your seeds to ensure they remain viable for future planting.
Allow your seeds to dry for at least 7-10 days in a cool, dark place with low humidity. This will help prevent mold growth and improve seed longevity.
Store the dried seeds in airtight containers, preferably in a cool, dark environment. Ideal storage conditions include a temperature between 41°F to 50°F (5°C to 10°C) with humidity levels around 20-30%. Using silica gel packets can help control moisture levels.

Even after a successful harvest, monitoring the viability of your seeds is crucial for future growth.
To ensure your seeds are viable, perform a germination test. Place a few seeds between damp paper towels and keep them in a warm, dark place. If they sprout within 48 to 72 hours, they are still good for planting.
Keep an eye on your stored seeds throughout the year. If you notice any signs of moisture or mold, take immediate action to address the issue.

Harvesting Green Crack seeds can come with challenges. Here are some common issues and their solutions:
If your seeds are underdeveloped or absent, it may be due to inadequate pollination or stress on the plant. Ensure you provide a stable growing environment and proper care during the flowering stage.
High humidity levels during harvest can lead to mold growth. Ensure you are harvesting in dry conditions and that your seeds are properly dried and stored.
Check for pests that can affect seed quality. Implement organic pest control measures to keep your plants healthy throughout their life cycle.

As you become more experienced in harvesting Green Crack seeds, you may want to explore advanced techniques to improve yield and seed quality.
Instead of harvesting all at once, you can selectively harvest mature seeds from different plants at staggered intervals. This allows you to monitor seed maturity and improve the overall quality of your harvest.
If you are interested in creating new strains or improving seed genetics, consider cross-pollinating your Green Crack plants with another compatible strain. This technique can introduce desirable traits and improve your overall harvest.
In addition to harvesting seeds, cloning your Green Crack plants can be an effective way to ensure you have a consistent crop year after year. Cloning allows you to replicate the genetic material of your best plants.
Successfully harvesting Green Crack seeds in Canada involves understanding the plant’s life cycle, particularly during the flowering stage when seeds mature. Timing your harvest in late summer to early fall is key, with pistils turning brown and trichomes becoming cloudy indicating readiness. Use proper tools like pruning shears and gloves to harvest, and ensure seeds are dried for 7-10 days in a cool, dark place to prevent mold. Store dried seeds in airtight containers with controlled humidity for long-term viability. To test seed viability, perform a germination test. Advanced techniques like selective harvesting and cross-pollination can further improve seed quality and yield.
The best time to harvest Green Crack seeds is in late summer to early fall, when about 70% of the pistils have turned brown and the trichomes are cloudy.
You will need pruning shears, gloves, and clean containers for collecting seeds.
Mature seeds are firm, dark in color, and can be found inside the buds, which should have brown pistils and cloudy trichomes.
Allow harvested seeds to dry in a cool, dark place for 7-10 days to prevent mold and maintain viability.
Store seeds in airtight containers in a cool, dark environment, with humidity levels around 20-30% for optimal longevity.
We ship and deliver world wide via USPS and various couriers.
We offer a wide range of secure and anonymous online payment options.
We care about you, our customer. Please contact us with any questions or concerns.
Find out more about the benefits of being a loyal and regular customer.
WE ARE EVERY GROWERS ONE STOP SHOP TO ACQUIRE PREMIUM CANNABIS SEEDS FOR SALE IN THE USA, CANADA AND AUSTRALIA

Farmers Lab Seeds 2024, | All Right Reserved
Seeds are sold as novelty items, souvenirs, and collectibles. They contain 0% THC. We encourage our customers to check the legislation in their Country, State, Province, and Municipality prior to purchasing items from our store. We do not provide growing information.
All seeds are sold as hemp, and lab tested under 0.3% THC. This product is not for use by or sale to persons under the age of 21. This product should be used only as directed on the label. It should not be used if you are pregnant or nursing. Consult with a physician before use if you have a serious medical condition or use prescription medications. A Doctor’s advice should be sought before using this and any supplemental dietary product. All trademarks and copyrights are property of their respective owners and are not affiliated with nor do they endorse this product.
These statements have not been evaluated by the FDA. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any disease. Individual weight loss results will vary. By using this site, you agree to follow the Privacy Policy and all Terms & Conditions printed on this site. Void Where Prohibited by Law.